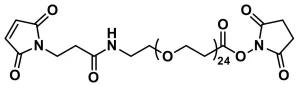
SPDP-dPEG®8-NHS ester, product number QBD-10376, is a medium-length (32 atoms), hydrophilic, non-immunogenic, heterobifunctional crosslinker that has the same functionality as the widely popular, but unfortunately hydrophobic, SPDP crosslinker. It contains an amine-reactive N-hydroxysuccinimidyl (NHS) ester on one end of the dPEG®8 linker, and a thiol-reactive SPDP (also known as OPSS) reactive group on the other end.
Among the most popular heterobifunctional crosslinking reagents used in bioconjugate chemistry are those compounds that conjugate molecules containing free amine groups with molecules that contain sulfhydryl groups. SPDP (N-succinimidyl 3-(2-pyridyldithio)-propionate) is one of the most popular versions of this type of crosslinker. Unfortunately, SPDP and its popular varieties (LC-SPDP and Sulfo-LC-SPDP) are hydrophobic molecules. When conjugated to biomolecules, care must be taken not to modify the target molecules too much, because this can precipitate the conjugate products.
By contrast, SPDP-dPEG®8-NHS ester, product number QBD-10376, is used like SPDP and its related hydrophobic products. However, precautions against overly modifying the target molecule are not necessary. The water-soluble dPEG® product will not cause the resulting conjugates to precipitate due to excessive hydrophobicity.
| Unit Size | 100 mg, 1000 mg |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 735.87; single compound |
| Chemical formula | C₃₁H₄₉N₃O₁₃S₂ |
| CAS | 1252257-56-9 |
| Purity | > 97% |
| Spacers | dPEG® Sp |
| Typical solubility properties (for additional information contact Customer Support) | Methylene chloride, Acetontrile, DMAC, DMSO or water. |
| Storage and handling | -20°C; Always let come to room temperature before opening; be careful to limit exposure to moisture and restore under an inert atmosphere; stock solutions can be prepared with dry solvent and kept for several days (freeze when not in use). dPEG® pegylation compounds are generally hygroscopic and should be treated as such. This will be less noticeable with liquids, but the solids will become tacky and difficult to manipulate, if care is not taken to minimize air exposure. |
Greg T. Hermanson, Bioconjugate Techniques, 2nd Edition, Elsevier Inc., Burlington, MA 01803, April, 2008 (ISBN-13: 978-0-12-370501-3; ISBN-10: 0-12-370501-0); See pp. 276-335 for general description and use of heterobifunctional crosslinkers, and the specific sample protocol for SPDP and LC-SPDP on pp. 286-288. See Greg’s extensive index on pp. 1192-1193 for references to a number and range of applications and their respective protocols.
Greg T. Hermanson, Bioconjugate Techniques, 3rd Edition, Elsevier, Waltham, MA 02451, 2013, ISBN 978-0-12-382239-0; See Chapter 18, Discrete PEG Reagents, pp. 787-821, for a full overview of the dPEG® products.
Cellular Delivery and Antisense Effects of Peptide Nucleic Acid Conjugated to Polyethyleneimine via Disulfide Linkers. Peter R. Berthold, Takehiko Shiraishi, and Peter E. Nielsen.Bioconjugate Chem., 2010, 21 (10), pp 1933–1938 September 27, 2010. DOI: 10.1021/bc1003586.
Cell number and transfection volume dependent peptide nucleic acid antisense activity by cationic delivery methods. Laia Llovera, Peter R. Berthold, Peter E. Nielsen and Takehiko Shiraishi. Artificial DNA, PNA & XNA 2012, 3 (1) pp 22-27 March 5, 2012. DOI: 10.4161/adna.19906.
In Situ Detection of Protein Complexes and Modifications by Chemical Ligation Proximity Assay. Rui Hong, Esteban Roberts, and Christopher Bieniarz. Bioconjugate Chemistry. 2016, June 1, 2016. DOI: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.6b00230.
Applicable patents and legal notices are available at legal notices.
Stay in the Loop. Join Our Online Community
Products
Ordering
About Us
Application
Resources

©Vector Laboratories, Inc. 2025 All Rights Reserved.
To provide the best experiences, we use technologies like cookies to store and/or access device information. Consenting to these technologies will allow us to process data such as browsing behavior or unique IDs on this site. Not consenting or withdrawing consent, may adversely affect certain features and functions. Privacy Statement
How do I Request a Quote?
To request a quote for products: