Azide Plus reagents is the most recent step in improving CuAAC reaction in complex media developed by scientists at Click Chemistry Tools. Azide Plus reagents contain a complete copper-chelating system in their structure, allowing for the formation of strong, active copper complexes that act simultaneously as both reactant and catalyst in the CuAAC reaction. This azide-copper complex reacts almost instantaneously with alkynes under diluted conditions. This unprecedented reactivity in the CuAAC reaction is of special value for the detection of low abundance targets, improving biocompatibility, and is also valuable for any other application where greatly improved S/N ratio is highly desired.
| Unit Size | 1 mg, 5 mg, 25 mg |
|---|---|
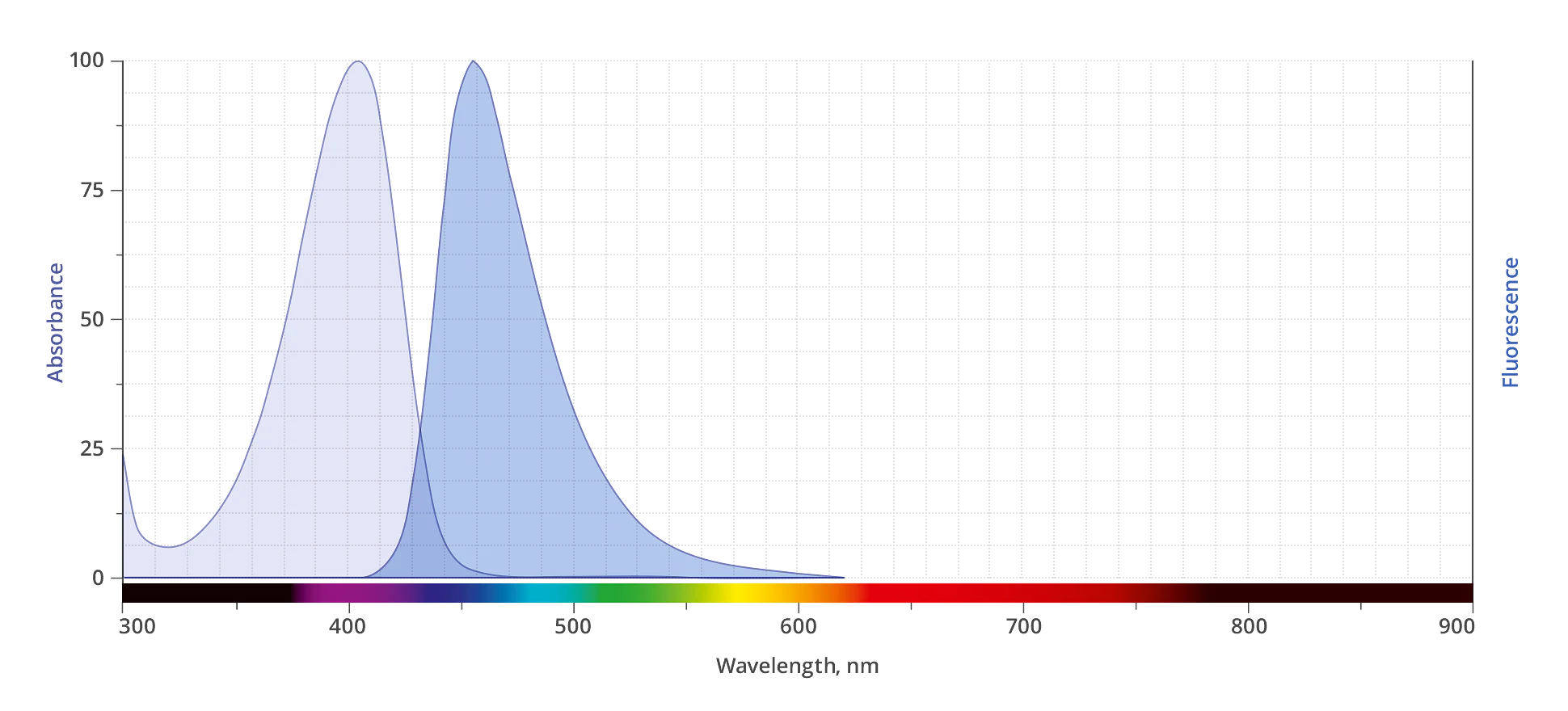
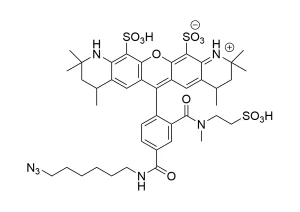
| Abs/Em Maxima | 403/453 nm |
| Extinction Coefficient | 30,000 |
| Spectrally Similar Dyes | Alexa Fluor® 405, CF® 405, Pacific Blue®, DyLight® 405 |
| Molecular weight | 580.55 |
| CAS | N/A |
| Solubility | Water, DMSO, DMF |
| Purity | >95% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | Yellow amorphous solid |
| Storage Conditions | -20°C. Desiccate |
| Shipping Conditions | Ambient temperature |
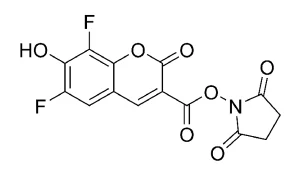
This is a general protocol for fixed/permeabilized cell imaging through a copper-catalyzed click reaction using the fluorescent Azide Plus reagent. We recommend using this protocol as a starting point for optimization of particular click chemistry procedures. We have found that a 1.5-3.0 μM concentration of Azide Plus reagent was optimal for most applications, including imaging of EdU incorporated into newly synthesized DNA and imaging of OPP labeled proteins without causing a high background signal. The optimal final concentration of the Azide Plus reagent is sample dependent and may range from 0.5 μM to 10 μM. Final concentrations below or above this range are also possible, and should be optimized per the specific application.
Table 1
| Reaction Component | Number of coverslipsor wells of a 96-well plate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 coverslip or 10 wells | 5 coverslips or 50 wells | 10 coverslips or 100 wells | 20 coverslips or 200 wells | |
| Reaction Buffer (Tris) | 888 µL | 4.4 mL | 8.9 mL | 17.8 mL |
| 50 mM Copper Sulfate | 10 µL | 50 µL | 100 µL | 200 µL |
| AZDye Azide Plus Solution (2 µM final concentration) | 2 µL | 10 µL | 20 µL | 40 µL |
| Sodium ascorbate | 100 µL | 500 µL | 1 mL | 2 mL |
| Total Volume | 1 mL | 5 mL | 10 mL | 20 mL |
This is a general protocol for labeling proteins in cell lysate through a copper-catalyzed click reaction using the fluorescent Azide Plus reagent. We recommend using this protocol as a starting point for optimization of particular click chemistry procedures. We have found that a 20 μM concentration of Azide Plus reagent was sufficient to label all alkyne-tagged proteins in the cell lysate without causing a high background signal. The optimal final concentration of the Azide Plus reagent is sample dependent and may range from 5 μM to 50 μM. Final concentrations below or above this range are also possible, and should be optimized per the specific application.
Applicable patents and legal notices are available at legal notices.
Stay in the Loop. Join Our Online Community
Products
Ordering
About Us
Application
Resources

©Vector Laboratories, Inc. 2025 All Rights Reserved.
To provide the best experiences, we use technologies like cookies to store and/or access device information. Consenting to these technologies will allow us to process data such as browsing behavior or unique IDs on this site. Not consenting or withdrawing consent, may adversely affect certain features and functions. Privacy Statement
How do I Request a Quote?
To request a quote for products: