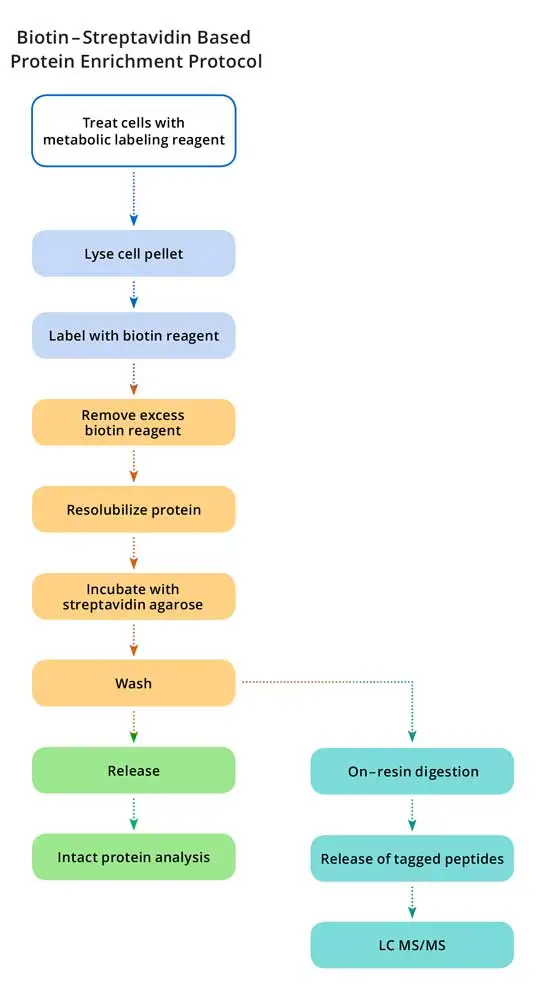
Extraordinary strength of the streptavidin-biotin interaction allows for efficient capturing of even highly dilute targets; however, it makes recovery of proteins from affinity resins challenging. Conventional methods to elute biotinylated proteins from immobilized avidin include the following: (i) denaturation of streptavidin by boiling the resin in a denaturing buffer that may include high concentrations of chaotropic salts, (ii) trypsin digestion of proteins while they are bound to the resin, or (iii) elution of proteins with excess free biotin. These protocols can co-elute contaminant proteins by releasing nonspecifically bound proteins and/or naturally biotinylated proteins concurrently with labeled proteins. In addition, some of these methods can cause elution of high levels of resin-based peptides along with the proteins of interest, resulting in further sample contamination.
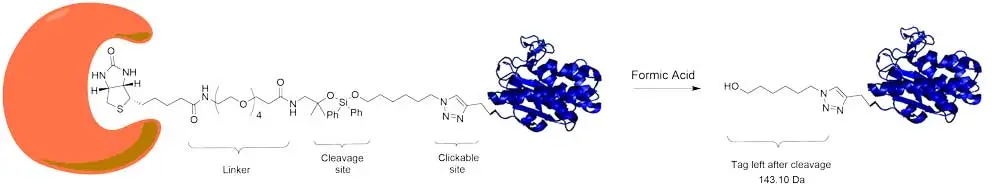
DADPS (dialkoxydiphenylsilane) Biotin Azide probes eliminate a major limitation of the streptavidin-biotin affinity purification. This reagent contains a biotin moiety linked to an azide moiety through a spacer arm containing a cleavable DADPS linker. Captured biomolecules can be efficiently released under mild conditions (10% formic acid, 0.5 h) and the small (143 Da) molecular fragment left on the labeled protein following cleavage. These features make the DADPS probe especially attractive for use in biomolecular labeling and proteomic studies.
| Enrichment target | Azide-modified proteins |
|---|---|
| Number of enrichments | 25 |
| Isolation technology | Biotin-streptavidin based capture |
| Storage Conditions | 4C |
| Shipping Conditions | Ambient temperature |
Applicable patents and legal notices are available at legal notices.
Stay in the Loop. Join Our Online Community
Products
Ordering
About Us
Application
Resources

©Vector Laboratories, Inc. 2025 All Rights Reserved.
To provide the best experiences, we use technologies like cookies to store and/or access device information. Consenting to these technologies will allow us to process data such as browsing behavior or unique IDs on this site. Not consenting or withdrawing consent, may adversely affect certain features and functions. Privacy Statement
How do I Request a Quote?
To request a quote for products: