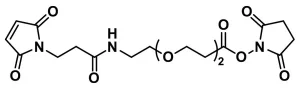
Bis-MAL-dPEG®11, product number 10397, is a medium-length, homobifunctional, crosslinking reagent that links two molecules (e.g., peptides, proteins) together via the thiol-maleimide reaction (also known as the thiol-Michael addition). The ends of the molecule are both functionalized with maleimidopropionate groups. The two reactive ends are separated by a single molecular weight, discrete polyethylene glycol (dPEG®) spacer.
The thiol-maleimide reaction, a type of click chemistry reaction, is an extremely popular way to conjugate molecules. The maleimide functional group rapidly reacts with sulfhydryl groups, and the reaction is chemoselective for sulfhydryls in the pH range of 6.5 – 7.5.
The polyethylene glycol (PEG) spacer between the two maleimide groups is a single molecular weight compound with a discrete chain length (thus the tradename dPEG®). This product is not made from a disperse polymer but is instead a single compound. Applications for this product include, among many others, studying cell internalization of crosslinked proteins; developing FRET immunoassays; and anchoring biomolecules to surfaces.
| Unit Size | 50 mg, 1000 mg |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 846.92; single compound |
| Chemical formula | C₃₈H₆₂N₄O₁₇ |
| CAS | 854753-78-9 |
| Purity | > 98% |
| Spacers | dPEG® Spacer is 49 atoms and 56.0 Å |
| Shipping | Ambient |
| Typical solubility properties (for additional information contact Customer Support) | Methylene chloride, DMAC or DMSO. |
| Storage and handling | -20°C; Always let come to room temperature before opening; be careful to limit exposure to moisture and restore under an inert atmosphere; stock solutions can be prepared with dry solvent and kept for several days (freeze when not in use). dPEG® pegylation compounds are generally hygroscopic and should be treated as such. This will be less noticeable with liquids, but the solids will become tacky and difficult to manipulate, if care is not taken to minimize air exposure. |
Greg T. Hermanson, Bioconjugate Techniques, 3rd Edition, Elsevier, Waltham, MA 02451, 2013, ISBN 978-0-12-382239-0; See Chapter 18, Discrete PEG Reagents, pp. 787-821, for a full overview of the dPEG® products.
Kinetics of endophilin N-BAR domain dimerization and membrane interactions. Benjamin R. Capraro, Zheng Shi, Tingting Wu, Zhiming Chen, Joanna M. Dunn, Elizabeth Rhoades, Tobias Baumgart. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2013, 288 (11) March 12, 2013. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.435511.
Enhanced Fluorescence resonance energy transfer immunoassay with improved sensitivity based on the Fab’-based immunoconjugates. Yoshiyuki Ohiro, Hiroshi Ueda, Norio Shibata, Teruyuki Nagamune. Analytical Biochemistry. 2007, 360 (2) pp 266-272. January 15, 2007. DOI: 10.1016/j.ab.2006.10.025.
X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy and Differential Capacitance Study of Thiol-Functional Polysiloxane Films on Gold Supports. Patrick A. Johnson and Rastislav Levicky. Langmuir. 2004, 20 (22) pp 9621-9627. September 28, 2004. DOI: 10.1021/la048458s.
Polymercaptosiloxane Anchor Films for Robust Immobilization of Biomolecules to Gold Supports. Patrick A. Johnson and Rastislav Levicky. Langmuir . 2003, 19 (24) pp10288-10294. October 30, 2003. DOI: 10.1021/la035102s.
Unfolding Mechanisms and Conformational Stability of the Dimeric Endophilin N-BAR Domain. Rui Jin, Michael Grasso, Mingyang Zhou, Ronen Marmorstein, and Tobias Baumgart. ACS Omega. 2021, Volume 6 Issue 32. 08/04/2021. DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.1c01905.
Applicable patents and legal notices are available at legal notices.
Stay in the Loop. Join Our Online Community
Products
Ordering
About Us
Application
Resources

©Vector Laboratories, Inc. 2025 All Rights Reserved.
To provide the best experiences, we use technologies like cookies to store and/or access device information. Consenting to these technologies will allow us to process data such as browsing behavior or unique IDs on this site. Not consenting or withdrawing consent, may adversely affect certain features and functions. Privacy Statement
How do I Request a Quote?
To request a quote for products: