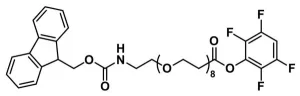
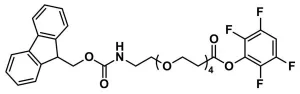
Fmoc-N-amido-dPEG®5-acid, product number QBD-10053, is one of a broad line of products designed for use in peptide synthesis. The short (19 atoms), discrete PEG (dPEG®) spacer is functionalized with a propionic acid group on one end and Fmoc-protected amine on the other. The product can be added to the N-terminus of a growing peptide chain or to a primary-amine-functionalized side chain of an amino acid such as lysine. The dPEG®5 spacer imparts water solubility to the peptide to which it is conjugated.
QBD-10053 permits our customers to insert a dPEG® spacer into a peptide chain using familiar Fmoc chemistry using solid phase or solution phase chemistry. The dPEG® compound can be inserted at either end of the peptide chain or in the middle of two amino acid sequences to provide a flexible linker between distinct functional peptides. Additionally, the dPEG® spacer can be used to provide spacing in a synthetic construct where steric hindrance is a problem. The amphiphilic nature of dPEG® products means that the construct gains hydrodynamic volume and water solubility while remaining soluble in organic solvent. The Fmoc protecting group removes easily with a solution of piperidine in N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF).
| Unit Size | 1000 mg |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 531.59; single compound |
| Chemical formula | C₂₈H₃₇NO₉ |
| CAS |
882847-32-7
|
| Purity | > 98% |
| Spacers |
dPEG® Spacer is 19 atoms and 21.6 Å |
| Shipping |
Ambient |
| Typical solubility properties (for additional information contact Customer Support) | Methylene chloride, Acetontrile, DMAC or DMSO. |
| Storage and handling | -20°C; Always let come to room temperature before opening; be careful to limit exposure to moisture and restore under an inert atmosphere; stock solutions can be prepared with dry solvent and kept for several days (freeze when not in use). dPEG® pegylation compounds are generally hygroscopic and should be treated as such. This will be less noticeable with liquids, but the solids will become tacky and difficult to manipulate, if care is not taken to minimize air exposure. |
Greg T. Hermanson, Bioconjugate Techniques, 3rd Edition, Elsevier, Waltham, MA 02451, 2013, ISBN 978-0-12-382239-0; See Chapter 18, Discrete PEG Reagents, pp. 787-821, for a full overview of the dPEG® products.
Design of a modular tetrameric scaffold for the synthesis of membrane-localized D-peptide inhibitors of HIV-1 entry. J. Nicholas Francis, Joseph S Redman, Debra M Eckert, and Michael S. Kay. Bioconjugate Chemistry. 2012, 23 (6), pp 1252-1258. May 1, 2012. DOI: 10.1021/bc300076f.
Enhanced Cellular Uptake of Peptide-Targeted Nanoparticles through Increased Peptide Hydrophilicity and Optimized Ethylene Glycol Peptide-Linker Length. Jared F. Stefanick, Jonathan D. Ashley, and Basar Bilgicer. ACS Nano. 2013, 7 (9) pp 8115–8127. August 29, 2013. DOI: 10.1021/nn4033954.
Applicable patents and legal notices are available at legal notices.
Stay in the Loop. Join Our Online Community
Products
Ordering
About Us
Application
Resources

©Vector Laboratories, Inc. 2025 All Rights Reserved.
To provide the best experiences, we use technologies like cookies to store and/or access device information. Consenting to these technologies will allow us to process data such as browsing behavior or unique IDs on this site. Not consenting or withdrawing consent, may adversely affect certain features and functions. Privacy Statement
How do I Request a Quote?
To request a quote for products: