Copper-Free Click Chemistry (SPAAC)
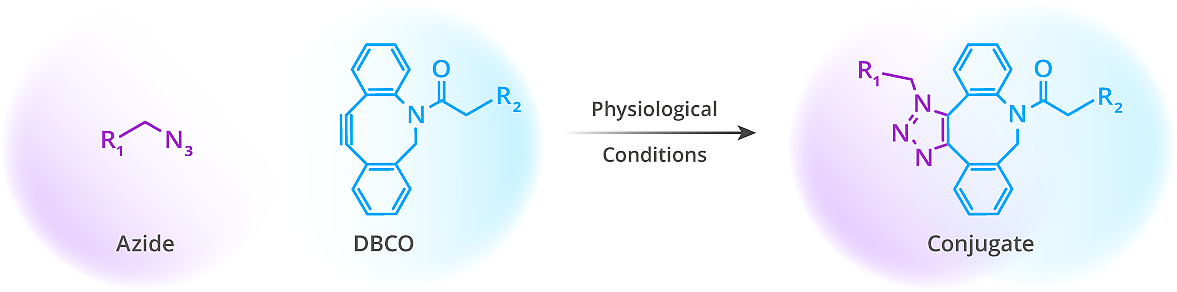
Strain-Promoted Azide-Alkyne Cycloaddition (SPAAC), also known as the copper-free click reaction, is a bioorthogonal method that allows for the efficient and exclusive reaction between cyclooctynes like dibenzocyclooctynes (DBCO) and azides.
This reaction is highly selective proceeding without interference from naturally occurring functional groups like amines or hydroxyls, and SPAAC does not require copper or other auxiliary reagents. The DBCO-azide reaction occurs rapidly in aqueous environments forming a stable triazole bond under physiological conditions. Due to its fast kinetics, biocompatibility, and stability in complex environments, a variety of biomolecules making it ideal for applications like live-cell labeling, in vivo imaging, bioconjugation, and targeted drug delivery. The mild conditions of this reaction ensure minimal disruption to biomolecules, allowing precise, non-toxic labeling in both live and fixed systems.
Vector provides a comprehensive selection of DBCO and azide reagents for SPAAC reactions delivering solutions for a wide range of experimental needs. Vector’s reagents ensure reliable performance for even the most sensitive biological applications.
Key Features of Copper-Free SPAAC Reactions:
Copper-Free Reaction:
SPAAC eliminates the need for copper catalysts, a key advantage for applications such as live-cell imaging and in vivo click chemistry.
High Specificity and Efficiency:
DBCO’s high reactivity with azides leads to rapid, selective conjugations without off-target effects minimizing impacts to biological systems.
Mild, Physiological Conditions:
SPAAC operates under physiological temperatures and pH making it highly suitable for use in living systems.
Versatile Compatibility:
SPAAC reactions are broadly applicable with DBCO-functionalized reagents capable of conjugating to azide-modified molecules such as proteins, peptides, nucleic acids, and small molecules.
Key Benefits Copper-Free SPAAC Reactions:
Non-Toxic and Biocompatible:
Since SPAAC is copper-free, it avoids the cytotoxicity commonly associated with CuAAC (Copper-Catalyzed Azide-Alkyne Cycloaddition) reducing cytotoxicity in sensitive biological systems such as live cells and tissues.
Preservation of Biomolecule Activity:
SPAAC's mild reaction conditions preserve the functionality of proteins and other biomolecules which is essential for assays where biological activity needs to be maintained.
Fast and Efficient Labeling:
The high reactivity of DBCO with azides ensures quick and efficient labeling improving throughput in experiments involving bioconjugation and in vivo imaging.
Applicable in Live and Fixed Systems:
SPAAC is highly effective in both live and fixed biological systems.
Broad Applicability of Copper-Free SPAAC Reactions:
- Live-Cell Labeling & In Vivo Imaging
- Biomolecule Conjugation (ex. proteins, peptides, glycans, nucleic acids, lipids, nanoparticles)
- Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs) and other targeted drug delivery
- Targeted Drug Delivery
- Metabolic Labeling
- Surface Functionalization
- Tissue Engineering
- Theranostics
- Fluorescence Imaging and Detection


Schematic representation of a SPAAC ligation reaction.