Vector Laboratories is closed for the President’s Day on Monday, February 19th. We will be back in the office on Tuesday, February 20th.
We will respond to emails upon our return. Have a wonderful day.
Menu
Vector Laboratories is closed for the President’s Day on Monday, February 19th. We will be back in the office on Tuesday, February 20th.
We will respond to emails upon our return. Have a wonderful day.
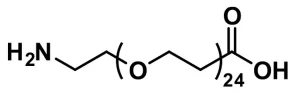
Amino-dPEG®24–t-butyl ester, product number QBD-10311, is a heterobifunctional, monodisperse polyethylene glycol (PEG) linker containing a single molecular weight and discrete length PEG (dPEG®) chain. One end of the dPEG® chain terminates with a carbonyl-reactive primary amine. The opposite end terminates with an amine-reactive, tert-butyl-ester-protected propionic acid. The t-butyl ester protecting group cleaves easily with trifluoroacetic acid (TFA), exposing a propionic acid moiety that forms amide bonds with primary amines upon activation. This compound is useful for supramolecular construction and building novel crosslinkers. Conjugates modified with QBD-10311 have improved water solubility and greater hydrodynamic volume.
The amine end of the molecule reacts with activated carboxylic acid esters (for example, N-hydroxysuccinimidyl or tetrafluorophenyl esters) to form an amide bond. Also, carboxylic acids can couple to the amine end of Amino-dPEG®24-t-butyl ester using a carbodiimide such as EDC, with or without an acylating agent such as N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS).
After working up the reaction to remove unreacted components and isolate the intermediate, trifluoroacetic acid is used to remove the tert-butyl ester and expose the propionic acid end group. The exposed carboxylic acid can then react further. For example, activation as the NHS or TFP ester is possible. Also, the acid can be coupled directly to an amine as described above.
| Unit Size | 100 mg, 1000 mg |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 1202.46; single compound |
| Chemical formula | C₅₅H₁₁₁NO₂₆ |
| CAS | 872340-65-3 |
| Purity | > 98% |
| Spacers | dPEG® Spacer is 76 atoms and 89.0 Å |
| Shipping | Ambient |
| Typical solubility properties (for additional information contact Customer Support) | Methylene chloride, DMAC, or DMSO. |
| Storage and handling | -20°C; Always let come to room temperature before opening; be careful to limit exposure to moisture and restore under an inert atmosphere; stock solutions can be prepared with dry solvent and kept for several days (freeze when not in use). dPEG® pegylation compounds are generally hygroscopic and should be treated as such. This will be less noticeable with liquids, but the solids will become tacky and difficult to manipulate, if care is not taken to minimize air exposure. |
Greg T. Hermanson, Bioconjugate Techniques, 3rd Edition, Elsevier, Waltham, MA 02451, 2013, ISBN 978-0-12-382239-0; See Chapter 18, Discrete PEG Reagents, pp. 787-821, for a full overview of the dPEG® products.
Tuning the affinity of amphiphilic guest molecules in a supramolecular polymer transient network. Maaike J G Schotman, Peter-Paul Fransen, Jiankang Song, Patricia T W Dankers. Royal Society of Chemistry. 2022. May 10, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1039/D2RA00346E
Applicable patents and legal notices are available at legal notices.
Stay in the Loop. Join Our Online Community
Together we breakthroughTM

©Vector Laboratories, Inc. 2024 All Rights Reserved.
How do I Request a Quote?
To request a quote for products: