Applications
NanoLINK streptavidin magnetic beads possess the highest biotin-binding capacity of any commercially available polymer-encapsulated streptavidin bead. These beads are particularly suited for high throughput robotic applications where high biotin loads must be immobilized and separated using a suitably strong magnet.
The beads can be used to immobilize:
- Biotinylated antibodies and other proteins
- Biotinylated dsDNA (gDNA, PCR products) or biotinylated aRNA
- Biotinylated oligonucleotides
The main advantage of using these ultra-high capacity beads is that it leads to a reduction in the overall particle mass required to immobilize a biotinylated sample. This in turn leads to reduced costs and lower non-specific background (NSB).
Applications include separation of biotin-labeled biomolecules such as biotin- labeled antibodies, genomic DNA, RNA, PCR products, oligonucleotides (e.g. biotinylated oligo (dT) or peptides. NanoLINK streptavidin magnetic beads are also ideal for generating single-stranded PCR templates (by removal of the unbiotinylated competing PCR strand), which allows for a dramatic increase in the efficiency of hybridization to complementary targets.
NanoLINK streptavidin magnetic beads also provide an affordable alternative for automated, high throughput immobilization processes that utilize 96-well magnets to affect multiplex binding and separation of nucleic acid or immunoassay biomolecules. NanoLINK beads are supplied at 10 mg/mL, with 1% solids, in nuclease-free water containing 0.05% sodium azide. There are no surfactants present although particles can be washed with water prior use to remove residual azide if desired.
Bead Characteristics
Percent Solids: NanoLINK streptavidin magnetic beads are packaged nominally at 1% solids (10 mg/mL) as measured using spectroscopic analysis set by their optical density at 600 nm versus a known mass standard of the same size.
Biotin Binding Capacity: The biotin binding capacity of NanoLINK streptavidin magnetic beads is measured in nmol/mg. Biotin binding is quantitatively measured by incubating a known mass of beads (0.5 mg) with a fluorescein-biotin standard solution for 60 minutes and quantifying the amount of residual unbound fluorescein-biotin left in solution versus negative control beads.
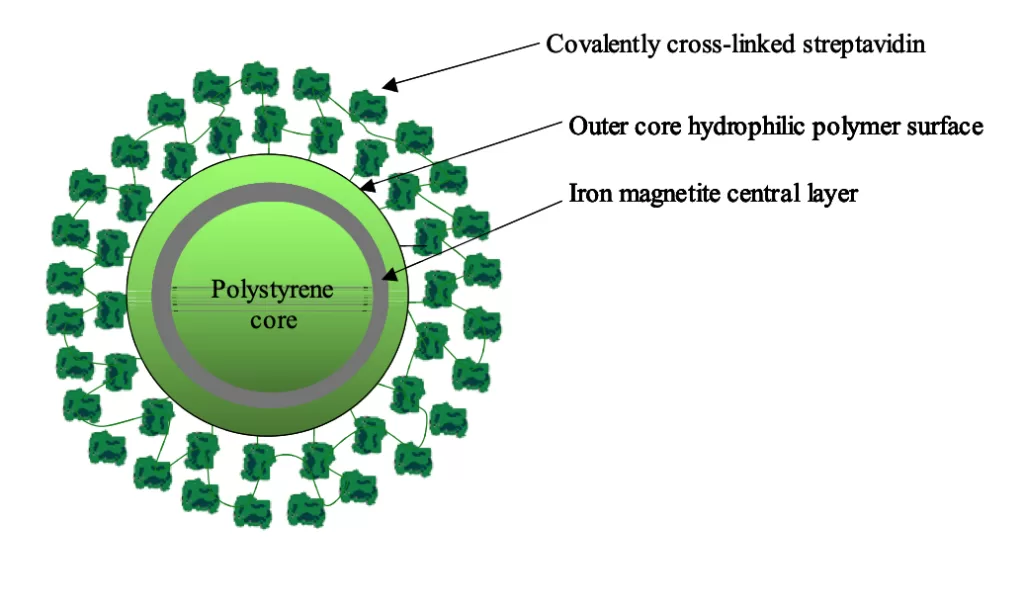
Size Distribution by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM): Scanning electron microscopy confirms a bimodal size distribution for NanoLINK Magnetic Beads. The streptavidin beads consist of a core polymeric particle ~ 850 nm surrounded by a population of similar but smaller polymeric beads ~ 150 nm.
Quality control: A sample of each NanoLINK batch is retained for biotin binding capacity and % solids analysis. The remainder is packaged, refrigerated, and preserved in nuclease-free water containing 0.05% sodium azide to prevent microbial contamination.
Cleaning: Surfactants are not added to this product and the particles are thoroughly washed with nuclease-free water containing 0.05% sodium azide prior to packaging. For some applications it may be desirable to remove residual azide using a brief wash.
Stability: Particles should be stored at 2-8o C. Do not freeze. If beads are settled, resuspend by suitable methods including: vortexing, rotary mixing, or swirling. NanoLINK streptavidin magnetic beads remain stable when stored at 2-8o C for 1 year.
Washing: NanoLINK streptavidin magnetic beads are washed by magnetic separation using commercially available magnetic stands. Magnetic stands are available in 50 mL, 15 mL, 1.5 mL, and 96-well plate formats from various vendors. NanoLINK beads are placed on a magnetic stand for 2-3 minutes and the clarified supernatant removed without disturbing the pellet.
Re-suspension: After long-term storage and settling of beads, it is best to resuspend the beads thoroughly to avoid any mild bead-to-bead aggregation.
NanoLINK References:
- Viktorovskaya O, Greco T, Cristea I, and S. Thompson. Identification of RNA Binding Proteins Associated with Dengue Virus RNA in Infected Cells Reveals Temporally Distinct Host Factor Requirements. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases 2016 Aug; 10(8): e0004921.
- Beaumont M, Tomazela D, and E. Escandón. Antibody-drug conjugates: integrated bioanalytical and biodisposition assessments in lead optimization and selection. AAPS Open volume 4, Article number: 6 (2018).
- Zhao Y, Valbuena G, Walker D, Gazi M, Hidalgo M, DeSousa R, Antonio J, Oteo Y.G., and A.R. Brasier. Endothelial Cell Proteomic Response to Rickettsia conorii Infection Reveals Activation of the Janus Kinase (JAK)-Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription (STAT)-Inferferon Stimulated Gene (ISG)15 Pathway and Reprogramming Plasma Membrane Integrin/Cadherin Signaling. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics. 15 (1) 289-304, 2016.